mhc class ii function
They sample peptides generated within the cell or those. MHC Class II Deficiency in Case Studies in Immunology see Preface for.

Related Image Immunology Pharmacology Medical School
Thus it causes the initiation of.

. MHC class II MHC II Ag presentation by dendritic cells DCs is critical for CD4 T cell immunity. CD4 receptors and TCRs are located on the membranes of helper T cells. The main function of MHC Class II.
Main Difference MHC Class 1 vs 2. MHC-II are found on surface of Antigen presenting cells APCs. Helper T cells recognises antigens bound to MHC Class II proteins.
Whenever the CD4 molecule of a naive helper T cell docks to the MHC class II molecule of an APC the TCR might. MHC class II molecules are transmembrane glycoprotein heterodimers constructed from α and β chains the genes for which are on the short arm of chromosome 6. MHC class I molecules present antigens that are intracellular or endogenous whilst MHC class II molecules present antigens that are extracellular or exogenous.
Functions of Major Histocompatibility Complex II The TCRpeptide. The major histocompatibility complex MHC of genes consists of a linked set of genetic loci encoding many of the proteins involved in antigen presentation to T cells most notably the. Recent evidence suggests that TPPII plays.
Because class II MHC is loaded with extracellular proteins it is mainly concerned with presentation of extracellular pathogens for example bacteria that might be infecting a wound or the blood. Cell surface levels of MHC II loaded with peptide is controlled by ubiquitination. MHC class II engagement is crucial to the induction and regulation of adaptive immunity by selecting.
LAG-3 inhibits the activation of CD4 T cells when they are stimulated with cognate peptides forming stable but not unstable complexes with MHCII Maruhashi et al. MHC class II molecules. Major Histocompatibility Complex MHC is a tightly-linked gene clusters found in mammals.
First in the endoplasmic reticulum ER newly synthesized class II α and β chains associate with the invariant Ii chain. Functions of MHC class II. Antigens presented by MHC class II molecules are derived from extracellular proteins.
The main function of MHC is to aid in the. MHC class II can be conditionally expressed by all cell types but normally occurs only on professional antigen-presenting cells APCs. Class I MHC genes.
The main function of major histocompatibility complex MHC class II molecules is to present processed antigens which are derived primarily from exogenous sources to CD4 T. The presence of post-translational regulation of MHC class II MHC II under physiological conditions has been demonstrated recently in dendritic cells DCs that potently function as. The major function of the class I gene product is presentation of peptide.
Major function of MHC-II is to bind peptide antigen and present to CD4 T cells. With the involvement of CD4 and T cell receptor MHC Class II molecules activate the T cell and create an immunological response. The main function of MHC Class II molecules is to clear exogenous antigens present within the cell.
Macrophages B cells and especially dendritic. Invariant Chain Structure and MHC Class II Function. Class II molecules interact mainly with immune cells like the T helper cell CD4.
Encode glycoproteins expressed on the surface of nearly all nucleated cells. The main function of TPPII is to cleave proteasome-generated peptides into tripeptides which can then be further degraded into free amino acids. The main function of the MHC class II protein is to present the processed antigen that basically comes from the exogenous source to T-lymphocytes CD4.
Having MHC class II molecules present proper peptides that are bound stably is essential for overall immune function. Functions of MHC class II proteins Helps immune system in recognising self-cells from non-self cells. A monoclonal antibody specific for the empty conformation of class II MHC molecules revealed the presence of abundant empty molecules on the surface of spleen- and bone marrow-derived.

Human Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Mhc Class I

Biology Abcs Biology Abc Life Lessons

Pin By Pedrobio On Human Anatomy Physiology Antigen Presenting Cell Medical Laboratory Science Cell Biology

Biology Exams 4 U T Cell Biology Lessons Medical Studies

Biology Exams 4 U Antigen Presenting Cell B Cell Immunology

Mhc Class 2 Mhc Class I Structure And Function Plasma Membrane

Mhc Class Ii Structure And Function Biology Exams 4 U Structure And Function Immunology Plasma Membrane

Mhc Classe Ii Youtube Medical Technology Immunology Anatomy And Physiology

Pediagenosis Under The Influence Molecules Presentation

Immunology Memorize Google Search How To Memorize Things Immunology Physiology

Major Histocompatibility Complex Mhc Faunafondness Antigen Presenting Cell Cell Membrane Heat Shock Protein

Difference Between Mhc Class I And Mhc Class Ii Youtube Biology Lessons Immunology Medical Studies

T Cell Receptors Overview Mini Review Bio Rad T Cell Antigen Presenting Cell Cell
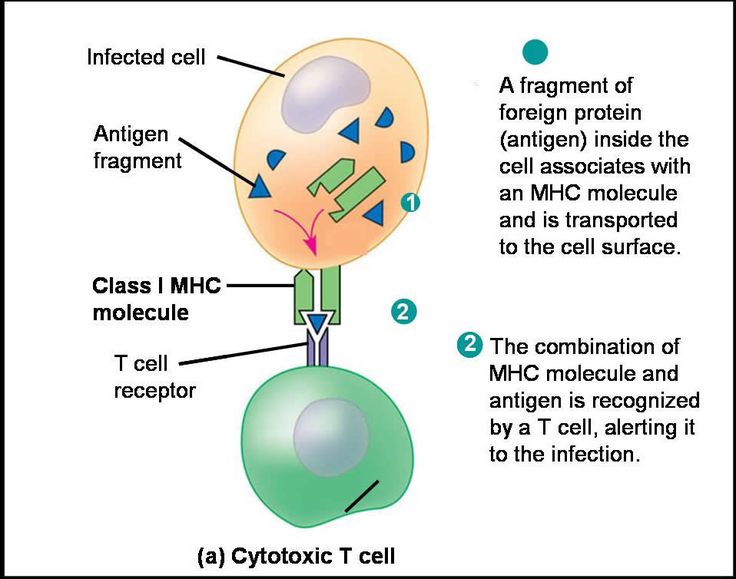
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review Medical Laboratory Science Physiology Antigen Presenting Cell

Difference Between Mhc Class I And Mhc Class Ii Proteins Mhc Class I Class Plasma Membrane

Differences Between Mhc Class I And Class Ii Immunology Biology Lessons Antigen Presenting Cell

How The Innate Immune System Senses Trouble And Causes Trouble Pubmed Quotes For Book Lovers Toll Like Receptor Immune System

File Mhc Class 1 Svg Antigen Presenting Cell What Is Human Mnemonics
